Metal stamping is a crucial manufacturing process, used across various industries to produce precise, high-quality metal stamping parts. These parts, varying from tiny stamped components to large structures, play a significant role in our day-to-day lives. Be it automobiles, electronics, aerospace, or appliances, stamped parts are everywhere.
In this comprehensive guide, we aim to dive deep into the world of stamped metal manufacturing, discussing the process, materials, types of parts, and much more. Whether you’re a seasoned professional or new to the field, this guide promises insights to enhance your understanding of metal stamping parts.
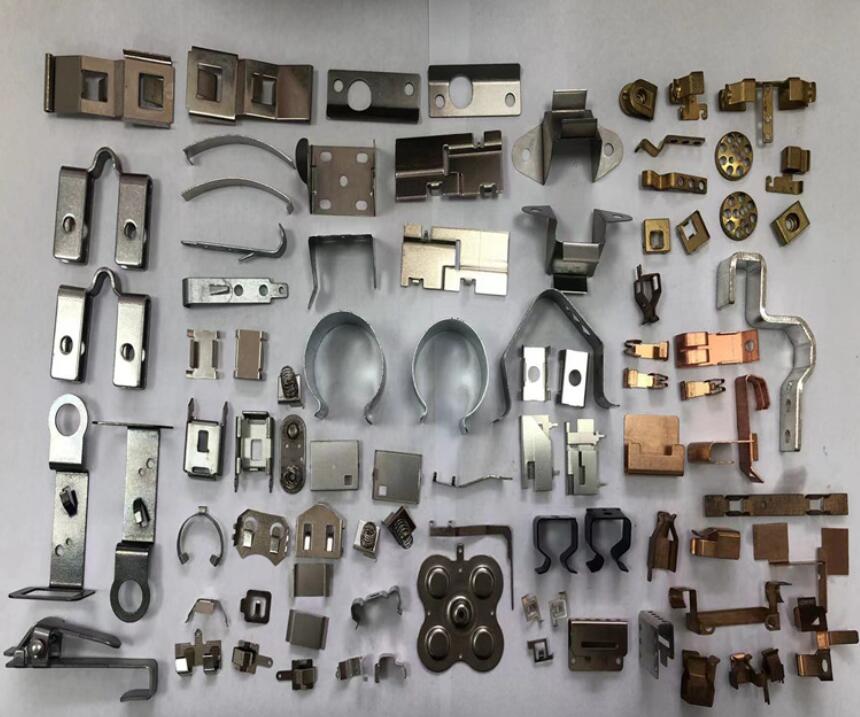

Understanding Metal Stamping
Metal stamping is an industrial process that utilizes dies and punch presses to transform sheet metal into various shapes and sizes. Predominantly, stamped steel, stamped aluminum, and stainless steel stamping parts are commonplace due to their durability and versatility. However, other materials like brass, copper, and bronze are also used based on specific requirements.
Key Elements in Metal Stamping Process
At the heart of the metal stamping process are the stamping dies, intricate tools that give shape to stamped metal products. These can range from simple single-stage dies to complex progressive dies used in progressive die stamping. Each type of die is suited to different applications and production volumes, making the correct choice of die crucial to producing high-quality stamped parts.
The raw materials, or metals, used in stamping also play a vital role. Stamped steel, stamped aluminum, and stainless steel stamping parts are prevalent, each offering unique properties. Steel is known for its strength, making it ideal for parts that need to withstand significant stress. Aluminum, on the other hand, offers the benefit of being lightweight yet sturdy, suitable for aerospace and automotive applications.
Finally, stamping presses apply force to the dies, creating the desired shape in the metal. Metal stamping presses can vary in their capacity and type, from mechanical to hydraulic, each suited to different tasks. The choice of press can have a significant impact on the efficiency and cost-effectiveness of the metal stamping process.
Different Types of Metal Stamping Parts
A. Automotive Parts

- Engine Components: Essential engine parts such as pistons, connecting rods, and crankshafts are often products of metal stamping. These stamped parts, made from robust materials like stamped steel or aluminum, need to withstand high temperatures and pressures.
- Chassis Parts: The vehicle’s chassis, which includes elements like the frame, cross members, and suspension mounts, relies heavily on stamped metal products. These components require high-strength materials like steel to ensure the vehicle’s structural integrity.
- Transmission Components: Gears, clutch plates, and housings are all key transmission components produced by metal stamping manufacturers. Precision and durability are paramount for these parts, making metal stamping an ideal manufacturing process.
The automotive metal stamping process caters to a wide range of vehicle types, from passenger cars to heavy-duty trucks, each requiring specific, high-quality metal stamping parts.
B. Electronics Parts
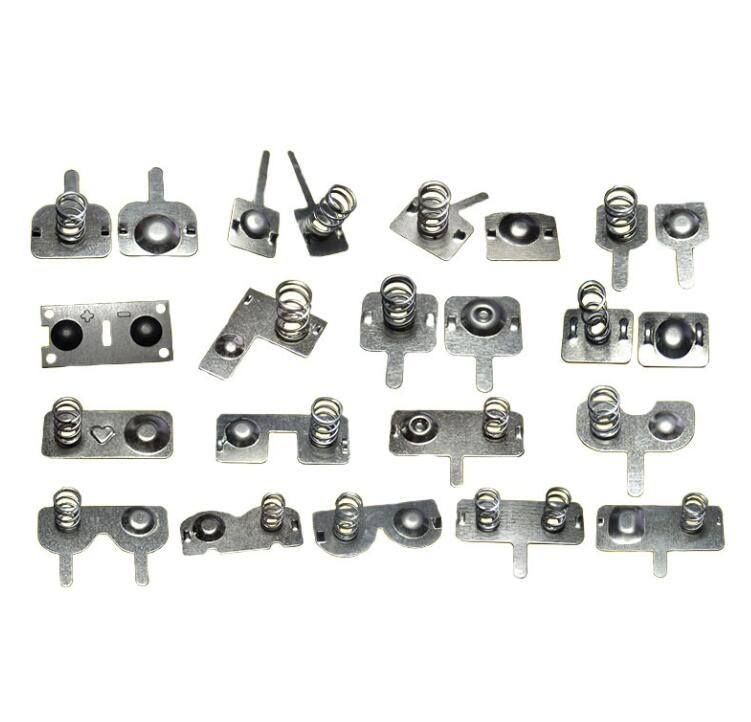

- Connectors: These small but crucial components, often made from stamped metal, provide secure and efficient electrical connections in a vast array of electronic devices. Their production often involves custom metal stamping to ensure precision and reliability.
- Terminals: Often produced using custom sheet metal stamping, terminals form the endpoints of a wire where it connects to a device or another wire. They must be highly conductive and resilient, often being made from materials such as stamped copper or brass.
- Metal Shields: These components play a critical role in protecting electronic devices from electromagnetic interference. Manufacturers often use stamped steel parts or stamped aluminum parts to produce these shields due to their effective shielding properties.
C. Aerospace Parts

Aerospace components often range from small parts like brackets, clips, and fasteners, to larger, more complex pieces such as panel controls and instrument enclosures. These parts are typically manufactured from stamped aluminum, titanium, or high-strength stamped steel, materials that offer superior strength-to-weight ratios crucial for aerospace applications.
Due to the stringent safety and performance standards in aerospace, metal stamping manufacturers often have to work with detailed specifications and tight tolerances. Custom metal stamping plays a significant role in creating components that meet these high standards.
To maintain the reliability and durability of these parts, the industry also utilizes stainless steel stamping parts for their corrosion resistance, a necessary feature considering the harsh environments these parts operate in.
D. Medical Device Parts
Surgical instruments, for instance, often feature stamped steel parts or stamped stainless steel parts for their strength and resistance to sterilization processes. These stamping parts might include scalpel handles, forceps, or specialized tools for specific surgical procedures.
Diagnostic equipment such as MRI machines or X-ray devices can contain various stamped components, including stamped aluminum parts for their excellent thermal conductivity and lightweight properties.
E. Industrial Machinery Parts
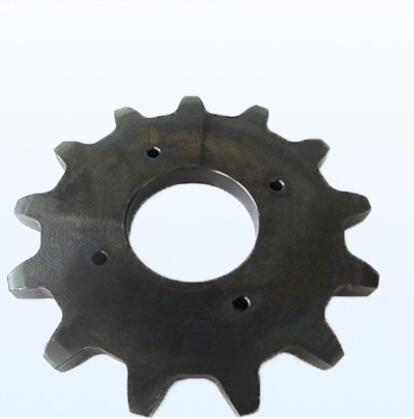

For heavy-duty applications might include structural components, brackets, or casings, all requiring high production metal stamping levels.
On the other hand, smaller stamped components, such as gears, shafts, or fasteners, are often made from stamped metal using custom metal stamping.
F. Consumer Goods Parts
In the appliance industry, metal stamped products often include components for washing machines, refrigerators, and ovens.
For consumer electronics, metal stamping parts might range from stamped metal parts for connectors and terminals to stamped components for heat sinks or shielding cases.
Key Considerations when Fabricating Metal Stamping Parts
A. Material Selection
Different metals offer different properties, making them suitable for different applications. For instance, stamped steel parts and stamped aluminum parts are often used in applications requiring high strength and durability, while stainless steel stamping parts are used where corrosion resistance is necessary.
B. Design Complexity
Complex designs might require advanced metal stamping techniques or custom metal stamping, while simpler designs could be achieved through production metal stamping.
C. Production Volume
High-volume orders may benefit from custom sheet metal stamping, which allows for efficient mass production. On the other hand, low-volume orders might benefit from the flexibility offered by small metal parts manufacturers.
Conclusion
In this comprehensive guide, we’ve explored the various types of metal stamping parts and their critical role across different industries. From automotive parts to consumer goods parts, metal stamping offers versatile solutions, tailored to specific applications.
Whether it’s stamped steel parts for the automotive industry, or intricate stamped components for medical devices, understanding these distinctions helps professionals in procurement, engineering, and design make informed decisions. So whether you’re sourcing stamped metal parts or partnering with a metal stamping manufacturer, keep this guide handy to navigate the complex world of metal stamping parts with confidence and clarity.
