Plasma Cutting Service
Custom Plasma Cutting for Prototyping and Production Part Fabrication.
- All uploads are secure and confidential.
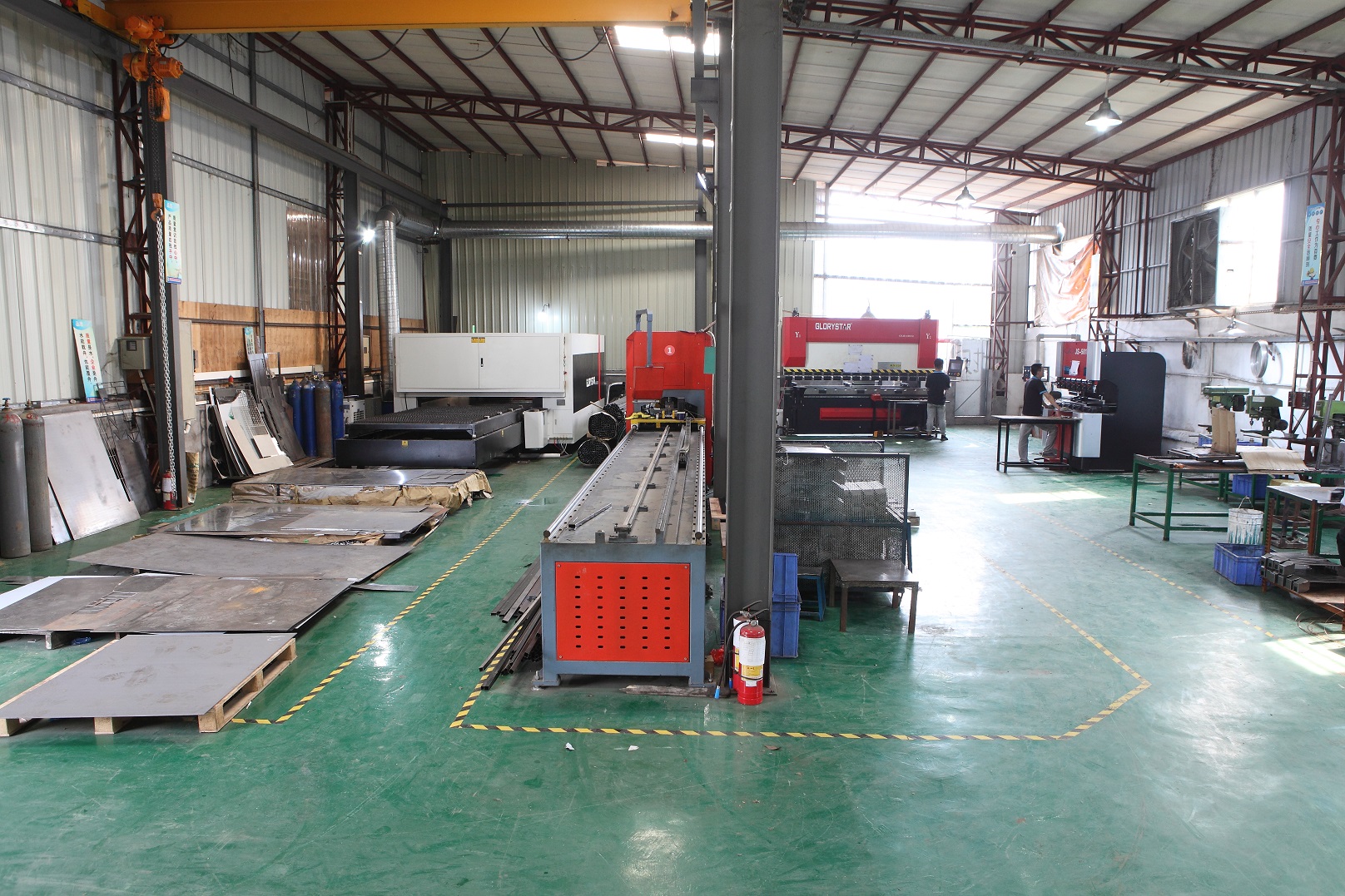

Our Plasma Cutting Capabilities
Chengli Hardware’s plasma cutting service supports a wide range of materials, including many types of metal, plastic, acrylic, foam, wood and carbon fiber. We support prototypes, low-volume and high-volume batches.
| Features | Capabilites |
|---|---|
| Max part size | 3000 x 2000 x 30mm |
| Dimensional accuracy | +/-0.127mm |
| Min lead time | 3 working days |
| Material thickness | 0.1-30mm |
What is Plasma Cutting?
Plasma cutting is a process that uses a high-temperature, ionized gas (plasma) to cut through electrically conductive materials such as steel, aluminum, brass, and copper.
The plasma cutter generates an electrical arc that passes through the gas, creating a high-temperature plasma stream. The plasma stream is then directed through a nozzle, which focuses the stream onto the workpiece, melting and cutting through the metal.
The process is often used in industrial manufacturing, automotive repair, and metal fabrication.

Advantages of Plasma Cutting
- Versatility and Flexibility: Plasma cutting could cut many conductive metal materials with thin and thick plates. It works great for cutting through irregular shapes, curved surfaces, and angled edges.
- Fast Speed:Its uses a plasma torch to create a jet of high-velocity ionized gas, which melts and blows away the material being cut. The speed of the ionized gas and the heat of the plasma arc allow for quick and efficient cutting.
- Cost-effective:Compared to other cutting methods like oxyfuel cutting, plasma cutting requires less setup time and can cut thicker materials in a shorter time. The reduced setup time, faster cutting speed, and lower equipment cost make plasma cutting a cost-effective option for industrial applications.
- Reduced heat distortion: Because plasma cutting uses a narrow and focused stream of ionized gas, it produces less heat, reducing the risk of heat distortion in the material being cut.
Challenges of Plasma Cutting
Limited Material Thickness: Plasma cutting is not suitable for cutting materials that are too thick, as the cutting quality may suffer.Normally 150mm is the limited.
- Limited material types: it is only suitable for cutting conductive metal materials, like aluminum, steel, brass, copper and stainless steel.
Noise: Plasma cutting can be quite loud, which may be an issue in certain settings.
Edge quality: The edge quality produced by plasma cutting may not be as precise and smooth as that produced by other cutting methods such as laser cutting.
How does Plasma Cutting Work?
Plasma cutting works by using a high-velocity jet of ionized gas, or plasma, to melt and cut through metal.
The process involves directing a stream of compressed gas through a small nozzle, while an electrical arc is created between the nozzle and the metal being cut.
The heat of the arc ionizes the gas, creating a plasma jet that can reach temperatures of up to 30,000 degrees Fahrenheit. The plasma melts and blows away the metal, resulting in a precise and efficient cut.
Normally there is three types of cutting process: High-Frequency Contact,Pilot Arc and Spring Loaded Plasma Torch Head
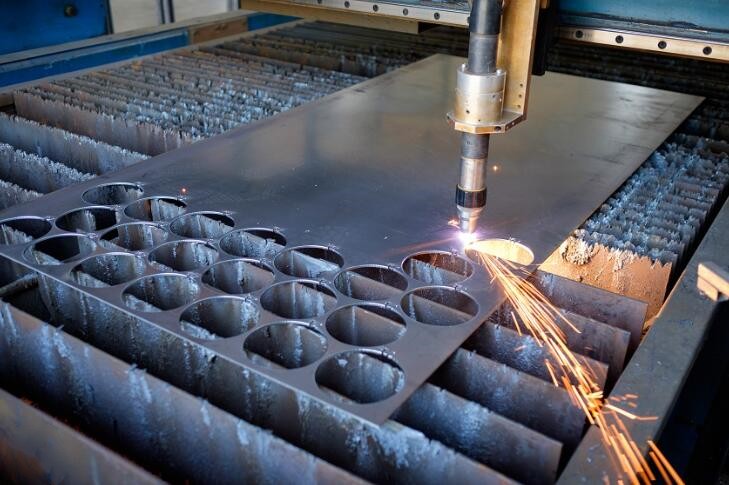

Plasma cutting Materials
Chengli Hardware works with a variety of metal materials, including stainless steel, aluminum, brass,steel and copper to provide customized solutions for your unique application.
| Aluminum | Stainless steel | Steel | Brass | Copper | Bronze | Titanium |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5052 | 301 | Steel A36 | C23000 | C101 | Bronze 220 | Grade 2 |
| 5083 | 17-4PH | S355 | C26000 | C110 | Bronze 510 | Grade 5 |
| 6061 | 304 | AISI 4130 | ||||
| 7075 | 316 | 1050 | ||||
| 2024 | 409 | 1065 | ||||
| 430 | Tool Steel | |||||
| 420 | Galvanized Steel |
Plasma Cutting Finish
We offer a variety of organic coating solutions to meet our customers’ special requirements. If you do not see the material finish combination you are looking for, please fill the quote sheet, and our experts will help you.
The metal stamping parts are typically deburred and cleaned, with a surface finish that is smooth but not polished or textured.It is characterized by visible tool marks, scratches.
Polishing can improve aesthetics and reduce surface roughness using a buffing or abrasive process.The surface rougness could reach to Ra0.8μm ,even Ra0.4μm.
A process where the surface of the metal is roughened or textured by blasting it with abrasive particles or media, such as sand or glass beads.This can help with grip or visual appeal.
Anodizing is a surface finishing process that produces a protective oxide layer on the surface of aluminum parts.
Type II( MIL-A-8625 Type II), provides corrosion resistance and can be done in different colors, such as clear, black, red, and gold.
On the other hand, Type III anodizing, also known as MIL-A-8625 Type III “hardcoat,” is thicker than Type II and creates a wear-resistant layer in addition to corrosion resistance.
Alodine is a chemical process, used to create a protective layer on the surface of the metal stamping parts, improving corrosion resistance and bonding capabilities.
This involves the surface of the metal stamping parts is brushed with an abrasive material, creating a textured or satin-like finish.
A layer of chromium is electroplated onto the surface of the metal stamping parts, creating a highly reflective and corrosion-resistant finish.
Passivation is a chemical process that removes surface contaminants and creates a passive layer on the surface of the metal part, protecting it from corrosion.
Electrophoresis coating, also named E-coating, is an electrocoating process where the metal is immersed in a bath of paint particles and an electric current is applied to create an even coating. Normally the color is black.
Phosphate Plated is a chemical and electrochemical reaction to form a phosphate chemical conversion film. This process is normally applied to steel materals.
Carburizing is a heat treatment process that introduces carbon into the surface layer of the metal to improve hardness and wear resistance.
A layer of zinc is electroplated onto the surface of the metal stamping parts, providing corrosion resistance and an attractive finish. We could supply white,blue,yellow,green colors.
Nickel electroplating is commonly used to improve the corrosion resistance, wear resistance, and surface finish of metal parts.
Nickel electroless plating is a chemical process that deposits a layer of nickel onto the surface of the metal part, creating a uniform and corrosion-resistant finish.
Powder coating is electrostatically applied to the metal stamping parts, which are then baked in an oven to create a durable and attractive finish. A wide variety of colors are available to create the desired aesthetic.
Liquid paint is applied to the surface of the metal stamping parts, providing an attractive finish but typically less durability than powder coating.
This involves the application of a layer of tin to the surface of the metal for improved corrosion resistance and solderability
Black oxide is a chemical process that creates a dark, corrosion-resistant finish on the surface of the metal part.
PVD is an industrial manufacturing process, i.e., vacuum coating, that gives products a beautiful metallic texture and excellent performance. It applies for metal and plastic material, a kind of expensive finishing process.Gold Plating provides good corrosion and tarnish resistance with excellent solderability
Gold Plating provides good corrosion and tarnish resistance with excellent solderability. Normally the thickness is 0.00002″ – 0.00005″.
Silk printing, also known as screen printing or serigraphy, is a printing technique that uses a woven mesh to support an ink-blocking stencil.
Plasma Cutting Tolerances
| Description | General Tolerance |
|---|---|
| Hole taper tolerance | 10% of material thickness |
| Distance Dimensions | ± 0.003” |
| Hole diameter | ± 0.003” |
| Maximum sheet size | 118x78.7x0.6" |
| Rotary Cutting tolerance | ± 1 degree |
| Edge Condition | Laser cut parts will have a matte, vertical striation on the edges. |
| Smallest feature | 0.002” |
| Minimum radius | 0.002” |
Plasma Cutting design guidelines
Need more support to optimize your project? Contact with our engineers
The kerf is the width of the laser beam, typically around 0.1-0.5 mm
The minimum distance between features on a part depends on the material thickness and the laser beam width. As a rule of thumb, the distance should be at least equal to the material thickness plus the kerf width.
.
As a rule of thumb, the detail size should be at least equal to the material thickness
The width should be at least equal to the material thickness plus the kerf width.
The depth should be less than the material thickness to avoid warping or bending of the material.
It is better to have a tolerance of at least +/- 0.1 mm to ensure a proper fit.
The text should be converted to curves or outlines to ensure that the font is preserved during cutting.
Width of at least 0.25 mm to ensure legibility.
Depth should be less than the material thickness to avoid warping or bending of the material.
Typically range from 0.5 mm to 25 mm,
Why Use Chengli's Sheet Metal Fabrication Services?
Thanks to our highly efficient process, we provide quick, accurate prototypes, small bath and mass production.
Competitive Prices
Our sheet metal fabrication services are cost-effective due to our advanced manufacturing processes, efficient production techniques, and experienced engineering team. We are committed to offering competitive pricing without sacrificing quality or delivery times.
Fast and Reliable Delivery
Quality parts for prototypes are delivered within our 5-day standard lead time. Quality parts for mass production are delivered in 12 days, even faster.
Manufacturing Capabilities
Our state-of-the-art facility has a wide range of cutting machines, bending machines, welding machines, and other advanced manufacturing equipment. We have the capability to produce complex parts with tight tolerances, and we offer a variety of secondary operations to complete your parts to your exact specifications.
Quality Assurance
We maintain rigorous quality control standards throughout our entire manufacturing process to ensure that every part we produce meets or exceeds customer requirements. Our quality management system is certified to ISO 9001:2015, and we utilize advanced inspection equipment and techniques to verify the accuracy and consistency of our products.
See What Our Customers Say About Us
See what our satisfied customers have said regarding how we fulfilled their requirements.



Plasma Cutting FAQ
Below you will find the answers to the most common questions about the plasma cutting process.
What is plasma cutting?
Plasma cutting is a process that uses a plasma torch to cut through various metals, such as steel, aluminum, and copper. The plasma torch generates an intense beam of ionized gas that melts and cuts through the metal.
What are some advantages of plasma cutting?
Plasma cutting offers several advantages, including high cutting speeds, the ability to cut through a variety of metals, and a relatively low cost compared to other cutting methods.
What is the difference between plasma cutting and laser cutting?
Plasma cutting uses a high-temperature ionized gas to melt and cut metal, while laser cutting uses a focused beam of high-intensity light. The choice between the two methods depends on the material thickness and required precision.
What thicknesses of material can be cut using plasma cutting?
The thickness of material that can be cut using plasma cutting depends on a variety of factors, including the type of material being cut and the power of the plasma cutter. Generally, plasma cutting can be used to cut materials up to several inches thick.
Plasma Cutting Application
From prototyping to production, Chengli has been a leading manufacturer of precision plasma cutting parts for a wide range of industries.
Gallery of Plasma Cutting Parts
We machine low-volume and high-volume production orders for customers in multiple industries: aerospace, automotive, defense, electronics, hardware startups, industrial automation, machinery, manufacturing, medical devices, oil & gas and robotics.